Today we are once again excited to have Dr./LtCol/All-around critical care guru Sam Galvagno. In addition to publishing in multiple major journals, defending the country, maintaining FOUR board certifications, AND maintaining a PhD in Clinical Research; Dr. Galvagno somehow finds time away from his job as Associate Director of the University of Maryland SICU to do what he does best: share his advanced knowledge of critical care. It is an honor and a privilege to share with you a lecture topic that Dr. Galvagno has spent many years researching: Osmotherapy. I assure you, no matter what your level of exposure is to this topic I GUARANTEE you will take away a TON of new clinical pearls!!
Podcast: Play in new window | Download
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | RSS
Key points
- Pearl #1: Egress of water = Loss of volume in the cranial vault
- Monroe-Kelley Doctrine!
- This is a BRIDGE to definitive therapy!
- Pearl #2: Water movement in the brain is NOT PASSIVE
- Need to physically alter the osmotic equilibrium with:
- A non-toxic, inert, object with COMPLETE exclusion from the brain
- Need to physically alter the osmotic equilibrium with:
- Pearl #3: A 1.6% reduction in brain volume = 90 ml of brain tissue saved!!
- An Osm of 300-320 will:
- Allow active egress of water from the brain tissue → decreased intracranial volume
- Improve elasticity of the cranial vault
- An Osm of 300-320 will:
- Pearl #4: There is NO JUSTIFICATION in withholding an osmolar agent due to lack of central access
- NO study shows significant harm is caused by using PIV
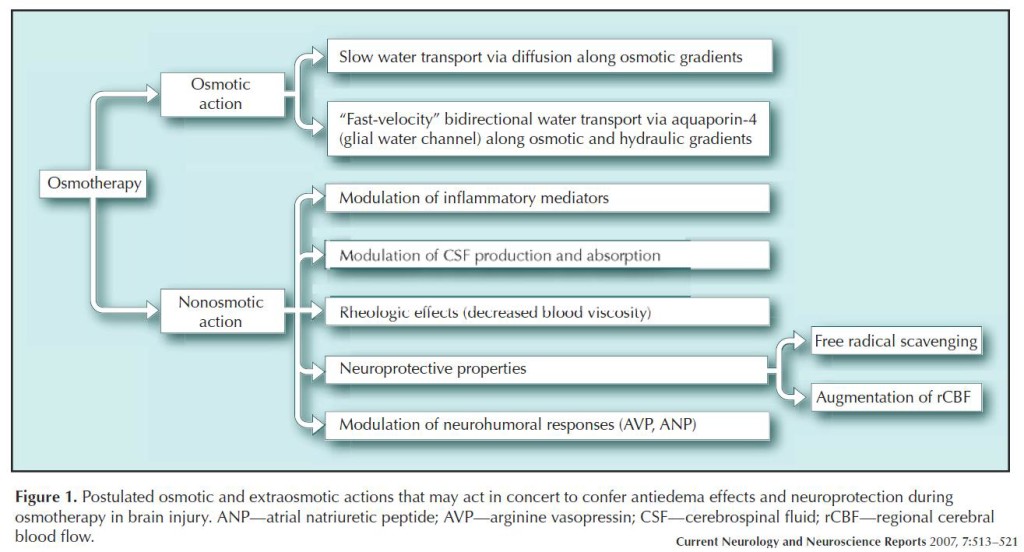
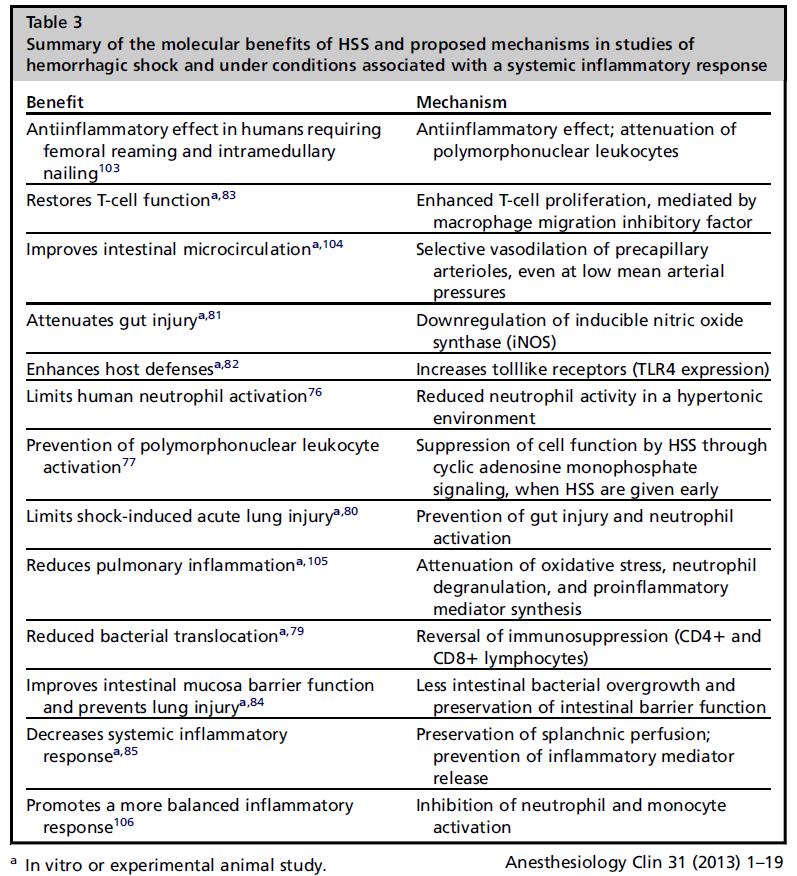
- Pearl #5: Osmotherapy agent effects extend beyond simply osmotic action:
Mannitol
- 1100 mOsm/L
- Dose: 0.25-1.5g/kg
- Takes 15-30 minutes for full effect, i.e.: takes time to lower ICP
- Lasts 2-4 hours
- Effects:
- Concentration gradient → egress of intracranial fluid
- Volume expansion (detrimental in CHF) → increased CO → improved CPP
- Vasoconstriction + decreased viscosity → improved CBF
- Proximal tubule diuretic (detrimental in AKI/CKD)
- Free radical scavenger
- Goal:
- DO NOT worry about a desired serum osm goal (i.e. <320…)
- Calculate Serum Osm Gap
- Renal failure rare with Osm Gap < 55!!
- Adverse effects:
- #1 side effect- diuresis → hypovolemia and hypotension
- Pulmonary edema, metabolic acidosis, hemolysis, AKI, hyperkalemia
Hypertonic Saline
- 3% 1027 mOsm/L, 5% 1711 mOsm/L, 23.4% 8000 mOsm/L
- Dose: 1-2 cc/kg/hr 3% or 4-6cc/kg/hr 2% (Ideal Body Weight)
- Lasts 48 to 72 hours
- Rise in Sodium can be augmented with simultaneous use of loop diuretic
- CAUTION:
- Chloride load leads to SEVERE hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis
- Sudden rise in sodium can lead to Central Pontine Myelinolysis (but…. only one documented case)
- Effects:
- Goal:
- Na level 145-160 (i.e. Osm 300-320)
- Adverse effects:
- In addition to acidosis and CPM, a rapid ICP drop can tear bridging veins and lead to a SDH
Hypertonic Saline vs. Mannitol
- No study has ever shown a remarkable difference (yet….)
Suggested Readings
- Vincent Cottenceau, Francoise Masson, Eugenia Mahamid, Laurent Petit, Venyamin Shik, Francois Sztark, Menashe Zaaroor, and Jean Francois Soustiel. Comparison of Effects of Equiosmolar Doses of Mannitoland Hypertonic Saline on Cerebral Blood Flowand Metabolism in Traumatic Brain Injury. Journal of Neurotrauma. October 2011, 28(10): 2003-2012.
- Diringer MN, Zazulia AR. Osmotic therapy: fact and fiction. Neurocrit Care. 2004;1(2):219-33.
- Galvagno SM Jr, Mackenzie CF. New and future resuscitation fluids for trauma patients using hemoglobin and hypertonic saline. Anesthesiol Clin. 2013 Mar;31(1):1-19.
- Bhardwaj A. Osmotherapy in neurocritical care. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2007 Nov;7(6):513-21.