Mojdeh S. Heavner, PharmD, BCPS, BCCCP, Assistant Professor, Critical Care, Department of Pharmacy Practice and Science at the U of Maryland School of Pharmacy and Jason J. Heavner, M.D., Chair, Department of Critical Care Medicine, University of Maryland Baltimore Washington Medical Center, present the weekly multi-departmental critical care fellows’ lecture on “Advances in Protocol-Driven Management of Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome in the ICU.”
Lecture Summary (by Dr. Jason Nam)
Alcohol use disorders (AUD) include:
- excessive alcohol intake
- alcohol abuse
- alcohol dependence
Alcohol use disorders (AUD) are associated with:
- 49% increased risk for mechanical ventilation
- Chronic alcohol intake leads to immune dysregulation
- Pneumonia is most common cause of sepsis in AUD patients
- Delirium tremens develops in 24-33% of AWS patients
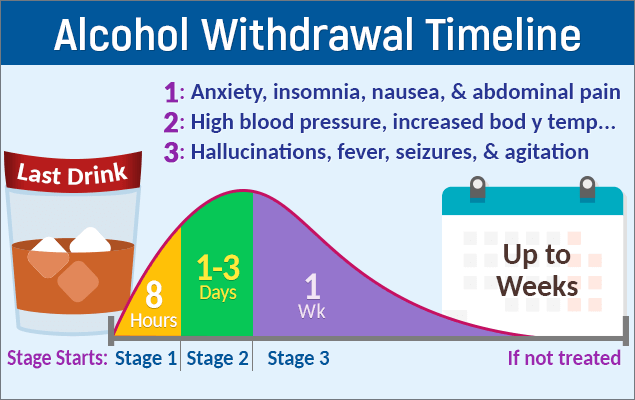
Timeline of alcohol withdrawal
Protocols in the ICU
- Advantages – reduce harmful variations in care, maximize efficiency, improve outcomes
- Disadvantages – minimize clinical judgment, encourage complacency, and stifle learning
- CIWA-Ar
- Symptom-triggered scoring.
- Validated in outpatient detox unit.
- Not studied in post-operative, medically complex, or ICU patients.
The Yale New Haven Experience
- Presenters’ experience of developing a novel ICU protocol at Yale New Haven.
- The protocol utilizes an objective administered scoring system (Modified MINDS). Dosing regimens derived from pharmacokinetic profile of each drug.
- Reiterates need for accurate diagnosis. Suggests adjuvant therapies specially to treat autonomic hyperactivity. Requires physician re-evaluation at critical times.
- Outcomes of YAWP:
- Significant reduction in ICU intubation and pneumonia.
- Significant use of adjuvants like clonidine.
- Annual cost-savings of $3.5M for the health system.
- Overall, YAWP implementation associated with significant improvements.
Conclusions
- Patient with AWS in the ICU can experience serious complications.
- Small, single center studies evaluating the use of ICU-specific AWS protocols, but more work is needed to establish a standard of care for ICU management.
- YAWP implementation has been associated with decreased odds of MICU intubation as well as significant cost savings for patients with AWS.
References
- Heavner, Jason J., et al. “Implementation of an ICU‐Specific Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome Management Protocol Reduces the Need for Mechanical Ventilation.” Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy 38.7 (2018): 701-713.
https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.proxy-hs.researchport.umd.edu/pubmed/29800507 - DeCarolis, Douglas D., et al. “Symptom‐driven lorazepam protocol for treatment of severe alcohol withdrawal delirium in the intensive care unit.” Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy 27.4 (2007): 510-518.
https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.proxy-hs.researchport.umd.edu/pubmed/17381377 - Littlefield, Audrey J., et al. “Correlation Between mMINDS and CIWA-Ar Scoring Tools in Patients With Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome.” American Journal of Critical Care 27.4 (2018): 280-286.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29961663
Uploaded by Sami Safadi, MD
Podcast: Play in new window | Download
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | RSS